Description
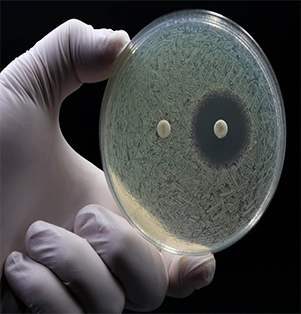
The Antibacterial Inhibition Zone refers to the area around an antibiotic disc where bacterial growth has been prevented due to the presence of an antimicrobial agent. This is observed in the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test, which is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics.
In this test, antibiotic-impregnated discs are placed on an agar plate inoculated with the bacteria of interest. After incubation, the bacteria typically form a layer on the plate, except for the areas around the discs where the antibiotic has diffused into the agar and inhibited bacterial growth. These clear areas are the zones of inhibition.