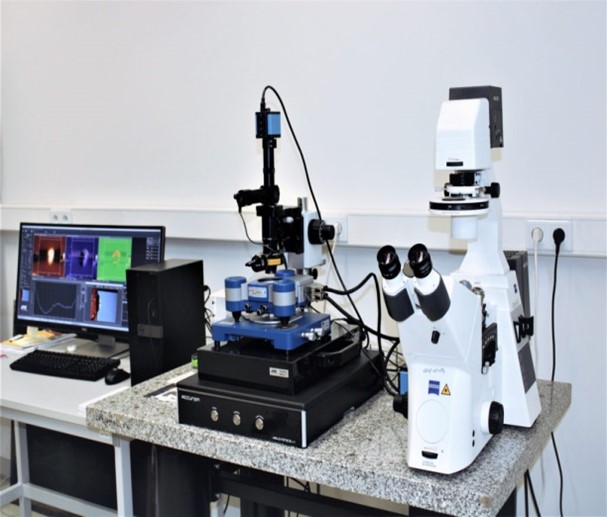
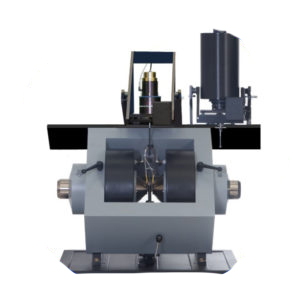
Description
The AFM/SPMDual Scope TM DS is an advanced Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) system.
AFM is a powerful tool that allows scientists and researchers to investigate surfaces at the nanoscale. Here are some common applications:
Surface Topography Imaging:
AFM excels at imaging surface structures with remarkable detail. By scanning a sharp tip over a sample, it creates a topographic map, revealing features such as bumps, valleys, and atomic arrangements. Researchers use AFM to study materials like semiconductors, polymers, biological tissues, and even individual molecules.
Materials Characterization:
AFM provides insights into material properties such as hardness, elasticity, and adhesion. It measures forces between the tip and the sample, allowing precise characterization.Scientists investigate thin films, coatings, and nanocomposites using AFM.
Biological Studies:
AFM plays a crucial role in life sciences. It allows imaging of biological samples in their native environment, including cells, proteins, and DNA. Researchers study cell membranes, protein interactions, and virus particles using AFM.
Nanomanipulation and Nanolithography:
AFM can manipulate individual atoms and molecules. Researchers use it to position nanoparticles, create nanostructures, and even modify surfaces at the atomic level.Nanolithography with AFM enables precise patterning for applications in electronics and photonics.
Electrical and Magnetic Characterization:
Conductive AFM (C-AFM) measures electrical properties of materials. It maps conductivity, charge distribution, and local current flow. Magnetic Force Microscopy (MFM) detects magnetic domains and studies magnetic materials.
Single-Molecule Studies:
AFM allows probing single molecules. Researchers stretch DNA, measure protein unfolding forces, and investigate molecular interactions.It’s a valuable tool for understanding biomolecular processes.
Environmental AFM:
Some AFMs operate in liquid or gas environments. Researchers study biological processes in physiological conditions. Environmental AFM is essential for understanding cell mechanics and interactions.
Remember, AFM is like a nanoscale detective, revealing hidden details and unraveling mysteries at the atomic and molecular levels. Its versatility makes it indispensable across various scientific disciplines